effector an eXplainable AI package for tabular data. It:
- creates global and regional effect plots
- has a simple API with smart defaults, but can become flexible if needed
- is model agnostic; it provides methods that can explain any underlying ML model
- integrates easily with popular ML libraries, like Scikit-Learn, Tensorflow, Pytorch or any other
- is fast, for both global and regional methods
- provides a large collection of global and regional effects methods
📖 Documentation | 🔍 Intro to global and regional effects | 🔧 API | 🏗 Examples
Installation
Effector requires Python 3.10+:
pip install effector
Dependencies: numpy, scipy, matplotlib, tqdm, shap.
Quickstart
Train an ML model
import effector
import keras
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
np.random.seed(42)
tf.random.set_seed(42)
# Load dataset
bike_sharing = effector.datasets.BikeSharing(pcg_train=0.8)
X_train, Y_train = bike_sharing.x_train, bike_sharing.y_train
X_test, Y_test = bike_sharing.x_test, bike_sharing.y_test
# Define and train a neural network
model = keras.Sequential([
keras.layers.Dense(1024, activation="relu"),
keras.layers.Dense(512, activation="relu"),
keras.layers.Dense(256, activation="relu"),
keras.layers.Dense(1)
])
model.compile(optimizer="adam", loss="mse", metrics=["mae", keras.metrics.RootMeanSquaredError()])
model.fit(X_train, Y_train, batch_size=512, epochs=20, verbose=1)
model.evaluate(X_test, Y_test, verbose=1)
Wrap it in a callable
def predict(x):
return model(x).numpy().squeeze()
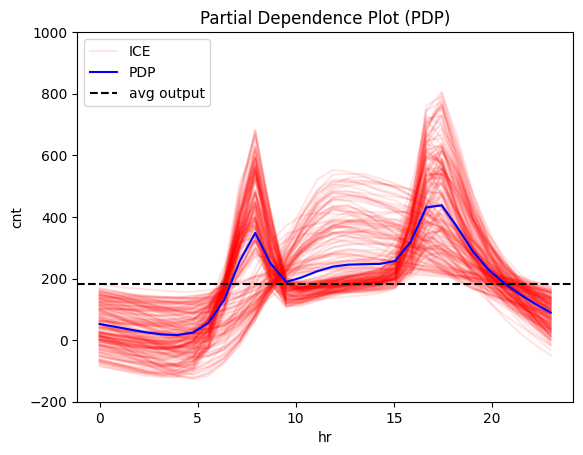
Explain it with global effect plots
# Initialize the Partial Dependence Plot (PDP) object
pdp = effector.PDP(
X_test, # Use the test set as background data
predict, # Prediction function
feature_names=bike_sharing.feature_names, # (optional) Feature names
target_name=bike_sharing.target_name # (optional) Target variable name
)
# Plot the effect of a feature
pdp.plot(
feature=3, # Select the 3rd feature (feature: hour)
nof_ice=200, # (optional) Number of Individual Conditional Expectation (ICE) curves to plot
scale_x={"mean": bike_sharing.x_test_mu[3], "std": bike_sharing.x_test_std[3]}, # (optional) Scale x-axis
scale_y={"mean": bike_sharing.y_test_mu, "std": bike_sharing.y_test_std}, # (optional) Scale y-axis
centering=True, # (optional) Center PDP and ICE curves
show_avg_output=True, # (optional) Display the average prediction
y_limits=[-200, 1000] # (optional) Set y-axis limits
)
Explain it with regional effect plots
# Initialize the Regional Partial Dependence Plot (RegionalPDP)
r_pdp = effector.RegionalPDP(
X_test, # Test set data
predict, # Prediction function
feature_names=bike_sharing.feature_names, # Feature names
target_name=bike_sharing.target_name # Target variable name
)
# Summarize the subregions of the 3rd feature (temperature)
r_pdp.summary(
features=3, # Select the 3rd feature for the summary
scale_x_list=[ # scale each feature with mean and std
{"mean": bike_sharing.x_test_mu[i], "std": bike_sharing.x_test_std[i]}
for i in range(X_test.shape[1])
]
)
Feature 3 - Full partition tree:
🌳 Full Tree Structure:
───────────────────────
hr 🔹 [id: 0 | heter: 0.24 | inst: 3476 | w: 1.00]
workingday = 0.00 🔹 [id: 1 | heter: 0.12 | inst: 1129 | w: 0.32]
temp ≤ 6.50 🔹 [id: 2 | heter: 0.06 | inst: 568 | w: 0.16]
temp > 6.50 🔹 [id: 3 | heter: 0.08 | inst: 561 | w: 0.16]
workingday ≠ 0.00 🔹 [id: 4 | heter: 0.12 | inst: 2347 | w: 0.68]
temp ≤ 8.76 🔹 [id: 5 | heter: 0.08 | inst: 1083 | w: 0.31]
temp > 8.76 🔹 [id: 6 | heter: 0.09 | inst: 1264 | w: 0.36]
--------------------------------------------------
Feature 3 - Statistics per tree level:
🌳 Tree Summary:
─────────────────
Level 0🔹heter: 0.24
Level 1🔹heter: 0.12 | 🔻0.12 (48.89%)
Level 2🔹heter: 0.08 | 🔻0.04 (31.11%)
The summary of feature hr (hour) says that its effect on the output is highly dependent on the value of features:
workingday, wheteher it is a workingday or nottemp, what is the temperature the specific hour
Let's see how the effect changes on these subregions!
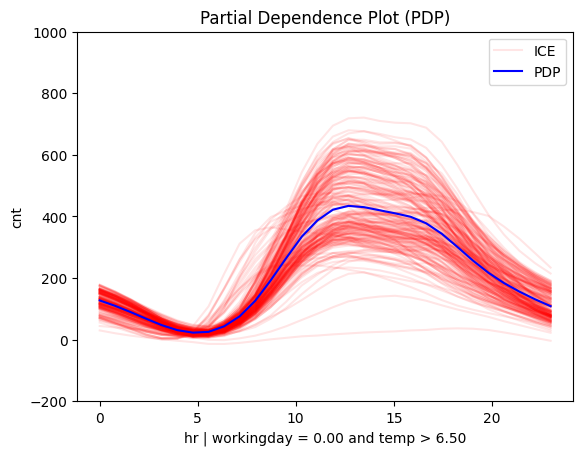
Is it workingday or not?
# Plot regional effects after the first-level split (workingday vs non-workingday)
for node_idx in [1, 2]: # Iterate over the nodes of the first-level split
r_pdp.plot(
feature=3, # Feature 3 (temperature)
node_idx=node_idx, # Node index (1: workingday, 2: non-workingday)
nof_ice=200, # Number of ICE curves
scale_x_list=[ # scale features by mean and std
{"mean": bike_sharing.x_test_mu[i], "std": bike_sharing.x_test_std[i]}
for i in range(X_test.shape[1])
],
scale_y={"mean": bike_sharing.y_test_mu, "std": bike_sharing.y_test_std}, # Scale the target
y_limits=[-200, 1000] # Set y-axis limits
)
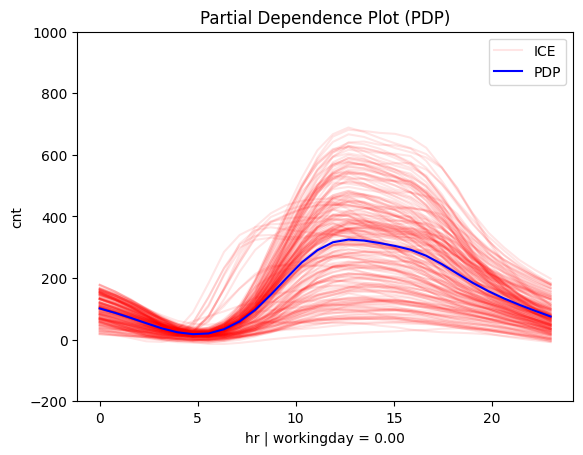 |
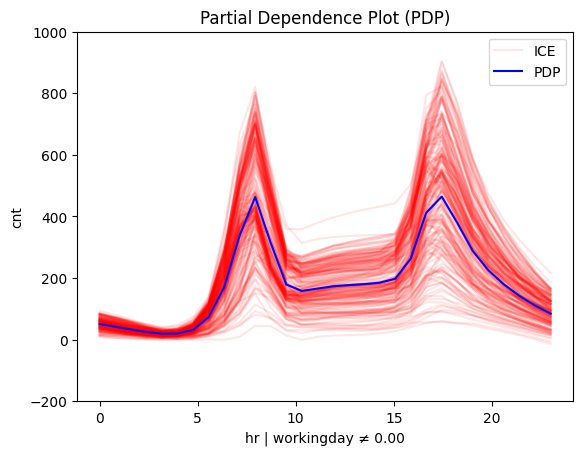 |
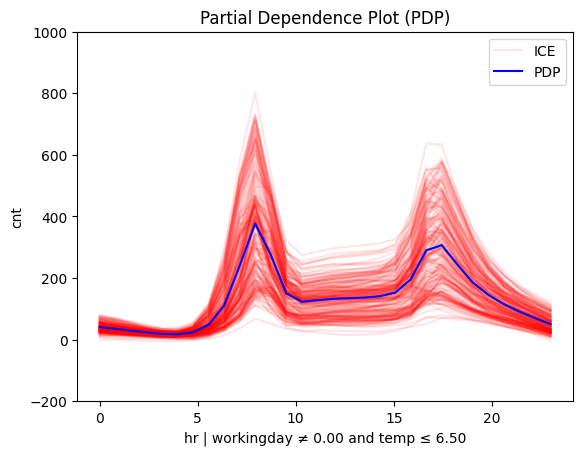
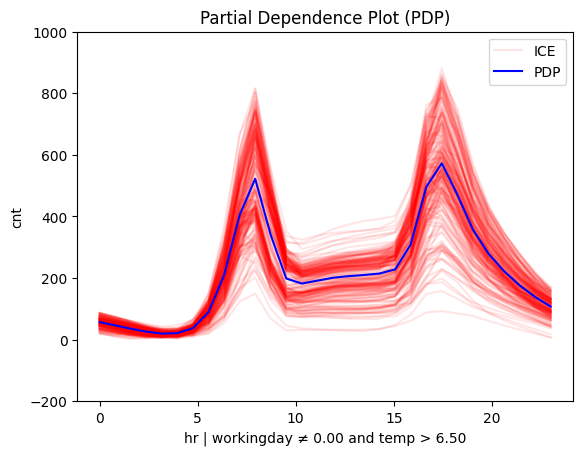
Is it hot or cold?
# Plot regional effects after second-level splits (workingday vs non-workingday and hot vs cold temperature)
for node_idx in [3, 4, 5, 6]: # Iterate over the nodes of the second-level splits
r_pdp.plot(
feature=3, # Feature 3 (temperature)
node_idx=node_idx, # Node index (hot/cold temperature and workingday/non-workingday)
nof_ice=200, # Number of ICE curves
scale_x_list=[ # Scale features by mean and std
{"mean": bike_sharing.x_test_mu[i], "std": bike_sharing.x_test_std[i]}
for i in range(X_test.shape[1])
],
scale_y={"mean": bike_sharing.y_test_mu, "std": bike_sharing.y_test_std}, # Scale the target
y_limits=[-200, 1000] # Set y-axis limits
)
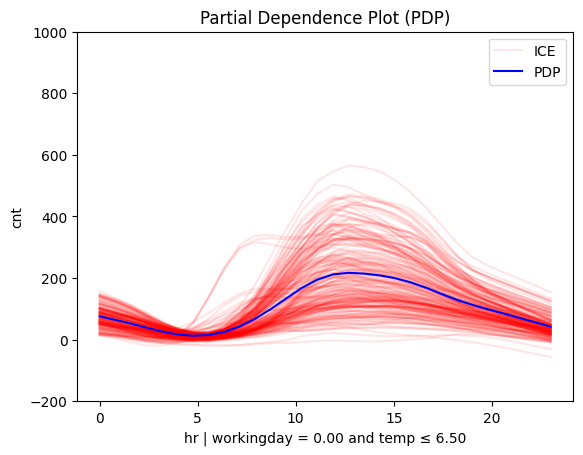 |
 |
 |
 |
Supported Methods
effector implements global and regional effect methods:
| Method | Global Effect | Regional Effect | Reference | ML model | Speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDP | PDP |
RegionalPDP |
PDP | any | Fast for a small dataset |
| d-PDP | DerPDP |
RegionalDerPDP |
d-PDP | differentiable | Fast for a small dataset |
| ALE | ALE |
RegionalALE |
ALE | any | Fast |
| RHALE | RHALE |
RegionalRHALE |
RHALE | differentiable | Very fast |
| SHAP-DP | ShapDP |
RegionalShapDP |
SHAP | any | Fast for a small dataset and a light ML model |
Method Selection Guide
From the runtime persepective there are three criterias:
- is the dataset
small(N<10K) orlarge(N>10K instances) ? - is the ML model
light(runtime < 0.1s) orheavy(runtime > 0.1s) ? - is the ML model
differentiableornon-differentiable?
Trust us and follow this guide:
light+small+differentiable=any([PDP, RHALE, ShapDP, ALE, DerPDP])light+small+non-differentiable:[PDP, ALE, ShapDP]heavy+small+differentiable=any([PDP, RHALE, ALE, DerPDP])heavy+small+non differentiable=any([PDP, ALE])big+not differentiable=ALEbig+differentiable=RHALE
Citation
If you use effector, please cite it:
@misc{gkolemis2024effector,
title={effector: A Python package for regional explanations},
author={Vasilis Gkolemis et al.},
year={2024},
eprint={2404.02629},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.LG}
}
Spotlight on effector
📚 Featured Publications
- Gkolemis, Vasilis, et al.
"Fast and Accurate Regional Effect Plots for Automated Tabular Data Analysis."
Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment | ISSN 2150-8097
🎤 Talks & Presentations
- LMU-IML Group Talk
Slides & Materials | LMU-IML Research - AIDAPT Plenary Meeting
Deep dive into effector - XAI World Conference 2024
Poster | Paper
🌍 Adoption & Collaborations
- AIDAPT Project
Leveragingeffectorfor explainable AI solutions.
🔍 Additional Resources
-
Medium Post
Effector: An eXplainability Library for Global and Regional Effects -
Courses & Lists:
IML Course @ LMU
Awesome ML Interpretability
Awesome XAI
Best of ML Python
📚 Related Publications
Papers that have inspired effector:
-
REPID: Regional Effects in Predictive Models
Herbinger et al., 2022 - Link -
Decomposing Global Feature Effects Based on Feature Interactions
Herbinger et al., 2023 - Link -
RHALE: Robust Heterogeneity-Aware Effects
Gkolemis Vasilis et al., 2023 - Link -
DALE: Decomposing Global Feature Effects
Gkolemis Vasilis et al., 2023 - Link -
Greedy Function Approximation: A Gradient Boosting Machine
Friedman, 2001 - Link -
Visualizing Predictor Effects in Black-Box Models
Apley, 2016 - Link -
SHAP: A Unified Approach to Model Interpretation
Lundberg & Lee, 2017 - Link -
Regionally Additive Models: Explainable-by-design models minimizing feature interactions
Gkolemis Vasilis et al., 2023 - Link
License
effector is released under the MIT License.